A VPN works by directing your internet traffic through a secure and encrypted tunnel that disguises your IP address and spoofs your network to its server location.
How VPN Works To Protect Your Online Privacy?
While a VPN performs multiple tasks to offer the highest grade of security and digital privacy, it also ensures your internet traffic can no longer be intercepted or tracked by anyone.
If you are wondering how VPN works, they simply work by routing the data that you send and receive through a secure, encrypted tunnel to mask your original IP address. This encryption conceals your internet activity and acts as a shield against digital threats.
While it enhances security and assists individual users in online activities, a business VPN brings several benefits to an organization through secure remote access for seamless remote operations.
What is a Webavior VPN, and How VPN Works?

Webavior VPN is an emerging yet highly ranked business-focused remote access VPN service that delivers best-in-class military-grade encryption along with a vast server network complemented by unlimited bandwidth for unrestricted usage.
It is a Remote Access VPN service that commits to a strict no-logs policy and exceptional privacy features for seamless remote operations.
However, while Webavior VPN offers the highest-grade encryption and safeguards your privacy, it is also essential to understand how VPN works and provide secure access. Read about the detailed functionality of A VPN below:
1. Establishing the Initial Connection to the VPN Server
The initial operation of a VPN service begins with the user’s device connecting to the VPN server.
When you log in and activate your VPN, it performs the user authentication to verify your credentials and performs a client-server handshake. This VPN handshake happens to negotiate the VPN security protocol to be used between the client and the server.
The server used is typically selected by the user or automatically by the VPN service, and it is located in a different geographical location from the various global servers provided by the VPN provider.
2. Creation of a VPN Tunnel for Protocol Selection and Key Exchange
After the initial connection is established, the VPN then creates a secure, encrypted tunnel to encrypt the user’s data that is being transmitted from the user’s device.
An encrypted tunnel is created using advanced tunneling protocols like WireGuard, OpenVPN, or IPsec, depending on the VPN provider’s security measures. These tunneling protocols assist in determining the levels of security, speed, and performance that will be obtained from the VPN servers.
The creation of an encrypted tunnel is then followed by the key exchange to create a shared secret key for a single-key encryption for all further communications.
3. Data Transfer to the VPN Server
The next step involves the transmission of the encrypted data to the VPN server. Subsequently, the user’s data that has already been encrypted is furthermore encapsulated or wrapped into fresh packets and sent via the encrypted tunnel.
IP address allocation works after the encrypted channel is created to integrate the client’s network and send these encapsulated packets to their designated destinations. The server performs the role of a mediator between the user’s device and the vast cyberspace.
4. Routing the Internet Traffic and Resource Access
The routing of internet traffic happens via 2 primary methods, including full tunneling and split tunneling. While a full tunneling VPN routes the complete internet traffic of the user, a split tunneling VPN encrypts a partial data to be sent and received by the user.
Since your ISP still has access to check that you are using a VPN service, the encryption ensures that they can not track or interpret the contents of your internet data. For a Business VPN, access to network resources is essential to ensure efficient productivity and enhanced privacy of the organization’s data.
5. Masking Your IP Address
The making of an IP address is an essential component of the working of a VPN service, as it substitutes your original IP address with its own.
This IP address spoofing manipulates the destination websites and servers to recognize the IP address of the VPN server as the actual IP address. The VPN tunneling protocols efficiently mask your original IP address to encapsulate your entire internet data.
6. Tunneling Back and Decrypting Data
The data that is sent by the destination server or webpage is initially received by the VPN server again, which later encrypts the data before delivering it to the user’s device.
Usually, the best remote access VPNs use exclusive obfuscation techniques for higher privacy of user data, which makes it indecipherable by the network administrators and regulatory authorities.
7. Final Decryption of Received Data
Lastly, the VPN client performs the decryption of the data transmitted through its endpoint. This decryption allows users to access data as if they were using the internet without intermediaries.
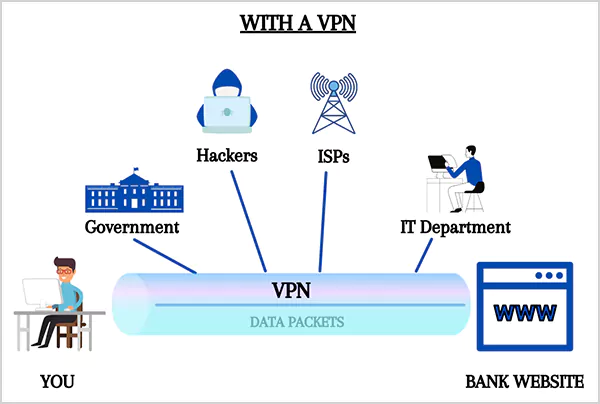
Subsequently, this workflow ensures the optimum security and the user’s confidentiality, as your ISP, government bodies, or even cyber criminals can not have access to your original IP address. Rather, they can only view and access the IP address created by your VPN service and its encrypted data.
Also Read: Industrial Remote Access VPN: Secure Connectivity for Remote Operations
Different Categories of VPN Services
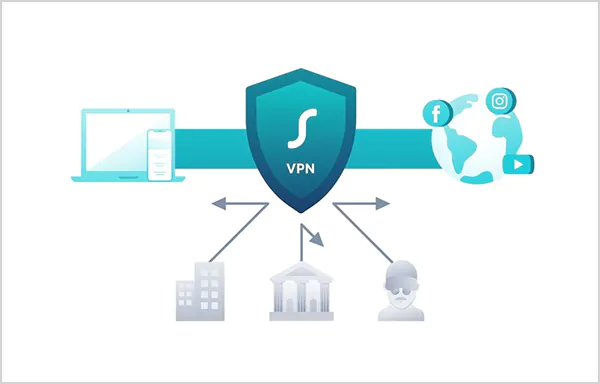
VPN services are categorized into different types depending on their operational and connection techniques, and the number of users utilizing their services. The primary types of VPN services include:
Remote Access VPN
Remote Access VPNs work as a security measure for organizations, as they allow their employees to securely establish a remote connection to the firm’s LAN and cloud network.
These services equip the remote employees to safely access the company’s server networks without the worry of data leaks and cyber attacks for optimized productivity.
Site-to-Site VPN
A site-to-site VPN offers the potential to connect the entire server networks of different organizations or an organization’s multiple divisions for streamlined management.
However, a site-to-site VPN and remote access VPN are different from each other, as a site-to-site VPN is used to connect 2 or more user or server networks, enabling efficiency for broad-scale operations.
Personal VPN
A personal VPN, or a consumer VPN, is a frequently used and widely recognized category of VPN that equips individual users to securely connect to a remote server by masking their IP address.
These services are used by individuals to enhance their digital security and increase streaming & gaming efficiency while gaining access to certain geo-restricted content.
VPN as a Service
VPN as a service is the Cloud VPN that is deployed in a cloud-based infrastructure, which equips its users with safeguarded access to the company’s resources and data.
It is different from traditional VPNs as it is hosted and deployed on the cloud for a stable and reliable connection with impressive scalability features.
Also Read: The Future of Remote Access: Is VPN Still the Best Solution?
Tips to Choose the Best VPN Service For You: A Buying Guide

While there are several VPN options available online, it becomes essential to select the ideal VPN that can cater to your needs and offer optimum security and privacy features. We have listed a few points that you should consider before your purchase.
- Optimum Security and Privacy Features: Opt for the Business VPN that provides advanced security and privacy attributes, including military grade encryption, transparent no-logs policy, kill switch, and obfuscated servers.
- Speed and Servers: Select the service that offers stable speed and reliable performance, along with a vast server network presence across numerous locations.
- Budget: We suggest initially understanding your budget and business requirements to select the ideal service that can provide secure remote access while offering optimal cost savings.
You can also refer to this chart to understand the key differences among the different types of VPN services to pick the most suitable service for your requirements.
| Attributes | Remote Access VPN | Site-to-Site VPN | Personal VPN | Cloud VPN |
| Connection Type | It connects a single-user device to the organization’s remote server | It connects the entire private network server to another private network | Individuals connect their devices to the VPN provider’s server network. | It connects the users to the organization’s resources and applications stored in the cloud. |
| Suitable for | It is suitable for off-site employees working remotely. | It best suits the needs of large-scale companies with extensive branch locations. | It is suitable for individuals who need a VPN for privacy, streaming, or gaming. | Small to mid-sized firms can use this to provide stable and secure remote cloud access. |
| Technology Support | SSL/TLS, IPsec, IKEv2, OpenVPN, WireGuard | IPsec, L2TP, OpenVPN, Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) | IPsec, IKEv2, OpenVPN, WireGuard | IPsec, IKE Fragmentation, Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) |
Also Read: Comparing VPN Security Across Different Platforms (Windows, macOS, Linux, Mobile) in 2025
Key Benefits of Using a VPN Service for Your Business
A business VPN brings several benefits to your organization for maximum productivity of employees, complemented by enhanced protection. The primary benefits of business VPN include:
- Maximum Security: Business VPNs offer optimum protection against digital threats and malware attacks by masking the IP address and using the highest-grade encryption to prevent data interception by your ISP, regulatory authorities, and cybercriminals.
- Secure Remote Access: These services equip the employees to remotely access the organization’s resources without worrying about security concerns, as they establish a safe and encrypted connection between the company’s servers and remote devices.
- Cost-effective Solutions: Business VPNs are an affordable and economical security tool that securely provides remote access to off-site employees without requiring several hardware deployments.
- Escaping Bandwidth Throttling: Your ISP usually slows down your internet speeds, which affects performance due to your heavy workload. These services help avoid bandwidth throttling and provide a stable connection for seamless operations.
Also Read: What is SOAR and its Importance in the Digital Age? Explore all the Critical Components of Security!
Conclusion
While this guide has explained how VPN works, it is also essential to understand how they assist in establishing secure remote access to the organization’s servers and resources for enhanced security and optimum productivity.
However, the performance speeds and level of protection that your VPN services offer depend on their security measures and choice of tunnelling protocols. Therefore, it is essential to select the ideal VPN based on your business requirements.
FAQs
How VPN works?
What are the different types of VPN?
The 4 major categories of VPN services include remote access VPN, site-to-site VPN, personal VPN, and Mobile VPNs. VPN as a Service, or cloud VPN, is another type of VPN that is hosted in a cloud-based infrastructure.
Does a VPN change and hide your IP address?
Yes, a VPN’s major functionality is to mask your IP address and your geographic location so that you can access websites without revealing your original IP address.